September 27, 2012
Kaspersky (Server) Anti-Spam: No Longer the Underdog; More Top Dog.
There’s an old Russian saying: As you start the New Year – that’s how you’ll spend the rest of it.
And this year started rather well for us: First, we were awarded Product of the Year by the Austrian testing lab AV-Comparatives; second, we broke the record on the number of points from Germany’s AV-Test.org; and third, we secured the top grade from Virus Bulletin in the UK. But after that pleasant start to the year things just got better, with the number of medals on our lapel going up and up and up! There were top marks in comparative testing of our proactive protection by Matousec; we were No. 1 in testing of our Application Control function by West Coast Labs; and we also secured excellent results in testing of our mobile security product (pdf) by PCSL. But we didn’t stop at serial-wins with our personal products; we also tore up the competition with our corporate ones; for example, in the August round of testing by AV-Test.org both KIS and KES were awarded 17 and 16 points, respectively – both higher than all the other competing solutions.
So, as you can see, in the first eight months of 2012 we’ve had rather a lot of good news. But never enough good news for me to forget to praise our ever faithful and pioneering AV lab (which praise I think it appreciates – so expect more victorious bulletins from the malware front soon!).
On this backdrop of positivity and optimism, the more deeper-delving observer might remark, “ok, your antivirus technologies come top-of-the-class across-the-board, but what about your NON-antivirus technologies – the important whistles and bells that add to a solution’s completeness and thus overall usefulness – like for example anti-spam?” All-righty: that’s what I’ll address in this post.
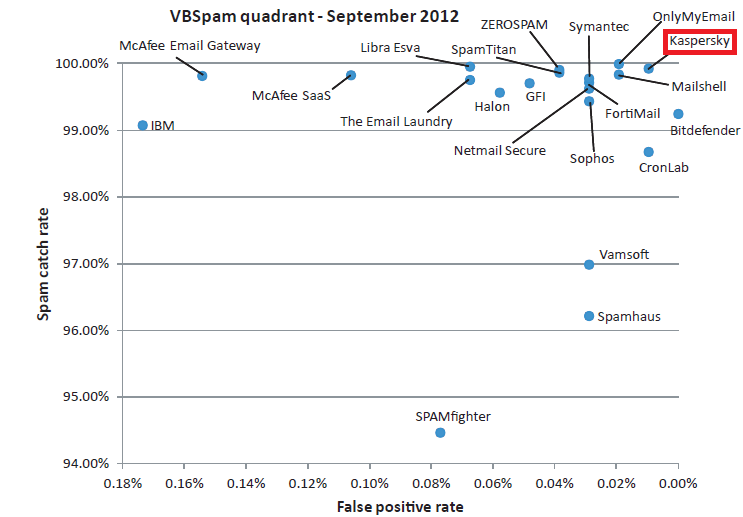
Just recently the results of Virus Bulletin’s VBSpam testing were released in which our new Kaspersky Linux Mail Security (KLMS) – unexpectedly for our competitors but quite expectedly for us – was among the winners – actually second – with an outstanding result of a 93.93% spam catch rate and 0.01% false positives. “Who wants to come second?” might come the refrain from those used to nothing but first place for KL. But in answer I’d say, “I do!” Here’s why…
More: It’s not for nothing I write ‘outstanding’ in italics……