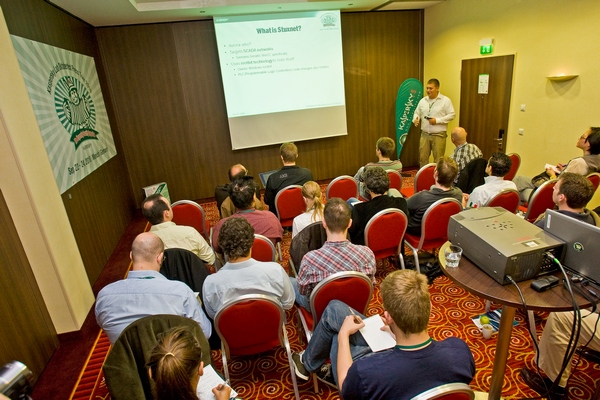
True to my word, herewith, the second installment of my new weekly (or so) series, ‘dark news from the cyber-side’, or something like that…
Today the main topic will be about the security of critical infrastructure; in particular, about the problems and dangers to be on the watch for regarding it. Things like attacks on manufacturing & nuclear installations, transportation, power grid and other industrial control systems (ICS).
Actually, it’s not quite ‘news’ here, just kinda news – from last week: fortunately critical infrastructure security issues don’t crop up on a weekly basis – at least, not the really juicy bits worthy of a mention. But then, the reason for that is that probably that most issues are kept secret (understandable, but worrying all the same) or simply no one is aware of them (attacks can be carried out on the quiet – even more worrying).
So, below, a collection of curious facts to demonstrate the current situation and trends as regards critical infrastructure security issues, and pointers to what needs to be done in face of the corresponding threats.
Turns out there are plenty of reasons to be bowled over by critical infrastructure issues…
If ICS is connected to the Internet, it comes with an almost 100% guarantee of its being hacked on the first day
The motto of engineers who make and install ICS is ‘ensure stable, constant operation, and leave the heck alone!’ So if a vulnerability in the controller is found through which a hacker can seize control of the system, or the system is connected to the Internet, or the password is actually, really, seriously… 12345678 – they don’t care! They only care about the system still running constantly and smoothly and at the same temperature!
After all, patching or some other interference can and does cause systems to stop working for a time, and this is just anathema to ICS engineers. Yep, that’s still today just the way it is with critical infrastructure – no seeing the gray between the black and the white. Or is it having heads firmly stuck in the sand?
In September last year we set up a honeypot, which we connected to the Internet and pretended was an industrial system on duty. The result? In one month it was successfully breached 422 times, and several times the cyber-baddies got as far as the Programmable Logical Controllers (PLC) inside, with one bright spark even reprogramming them (like Stuxnet). What our honeypot experiment showed was that if ICS is connected to the Internet, that comes with an almost 100% guarantee of its being hacked on the first day. And what can be done with hacked ICS… yes, it’s fairly OMG. Like a Hollywood action movie script. And ICS comes in many different shapes and sizes. For example, the following:
Nuclear malware
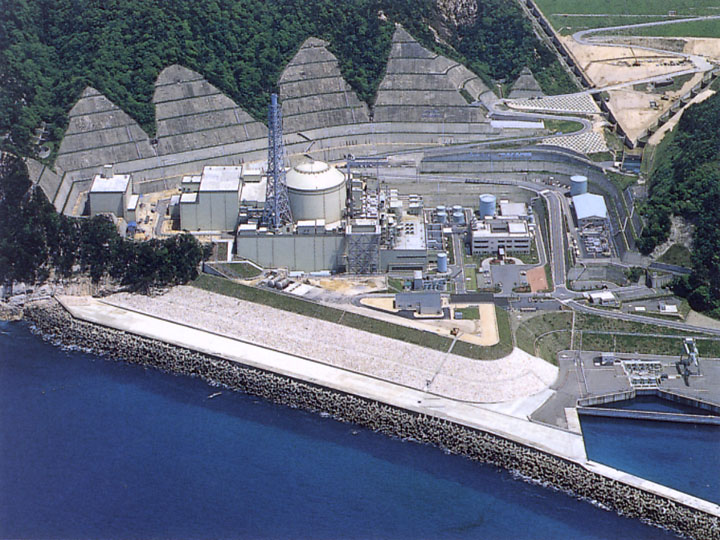 Source
Source
Read on: absence of light will only be the result of burned out bulbs and nothing else…


 Stylish stands
Stylish stands